An appendectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. It’s one of the most common emergency surgeries performed worldwide.
Why Is an Appendectomy Needed?
The most common reason why an appendectomy is conducted is appendicitis, which is the inflammation or infection of the appendix. If left untreated, the appendix can burst and cause serious complications likeperitonitis, an infection in the abdomen.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
- Sudden pain near the belly button, which then shifts to the lower right abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Abdominal swelling or tenderness
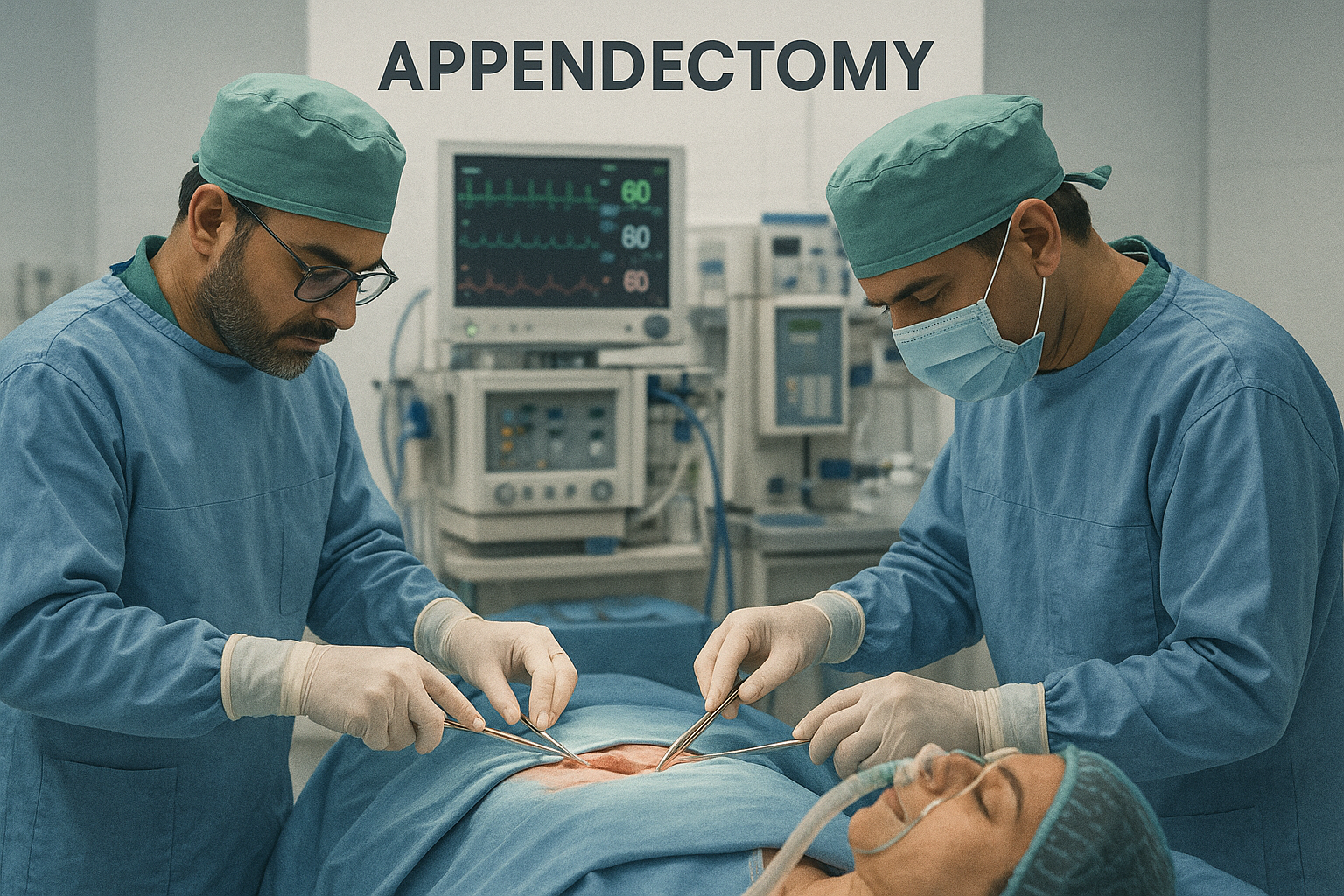
How Is an Appendectomy Performed?
There are two main types:
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy
It is a minimally invasive procedure in which small cuts are made to treat the patient. It promotes faster recovery and is less painful than an open appendectomy.
- Open Appendectomy
In an open appendectomy, larger incision in the lower right abdomen is made. This procedure is done if the appendix has ruptured or the infection is severe
The surgeon will choose the best method depending on the patient’s condition.
What to Expect After Surgery
The hospital stay is usually 1–2 days for laparoscopic and longer for open surgery.
There is mild pain and soreness around the incision. The patient be encouraged to walk soon after surgery to prevent complications.
Full recovery typically takes 1–3 weeks.
Recovery Tips
The patient should diligently follow doctor’s advice on wound care and medications. The patient should also avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity for a few weeks. A healthy diet to aid quicker healing is very important.
The patient should watch for signs of infection like fever, or even increased pain.
Final Words
An appendectomy is a safe and effective treatment for appendicitis. Early diagnosis and surgery can help prevent serious complications.
