When dealing with serious wounds, burns, or skin infections, cleaning the surface isn’t
always enough. Sometimes, damaged or dead tissue needs to be removed to help the body heal properly. This process is called debridement and is a critical part of advanced wound care.
What Is Debridement?
Debridement is the medical removal of dead tissue, infected tissue or foreign material or debris from a wound, burn, or infected area.
Removing this tissue helps reducing the infection risk, promote faster and cleaner healing and prepare the area for skin grafts or other treatments if needed.
When Is Debridement Needed?
Debridement may be recommended for non-healing wounds like diabetic ulcers or bedsores, severe burns where tissue is visibly dead, infected wounds with pus, foul odour, or blackened tissue or after traumatic injuries with debris, dirt, or dead skin.
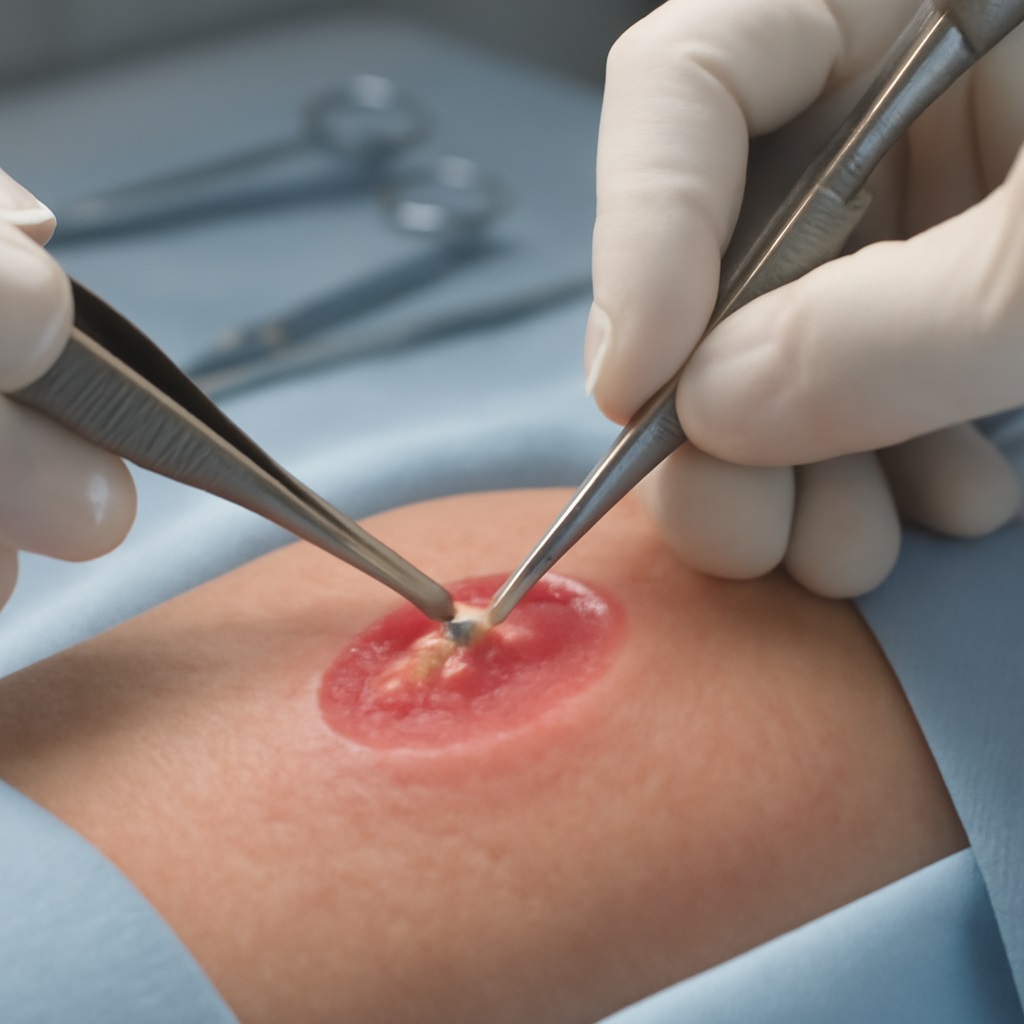
Types of Debridement
1. Surgical Debridement
It is quick and precise removal using scalpels or surgical tools and is often done under local or general anaesthesia. It is common in infected wounds or deep burns.
2. Mechanical Debridement
Mechanical debridement uses gauze, dressings, or water irrigation to remove tissue. The procedure may be simple but may be uncomfortable.
3. Enzymatic (Chemical) Debridement
Special creams or enzymes are used to dissolve dead tissue gradually. It is often used for chronic wounds or for patients who can’t undergo surgery.
4. Autolytic Debridement
It uses the body’s natural enzymes under moist dressings. It is painless but is a slower
process. It is suitable for smaller or less infected wounds.
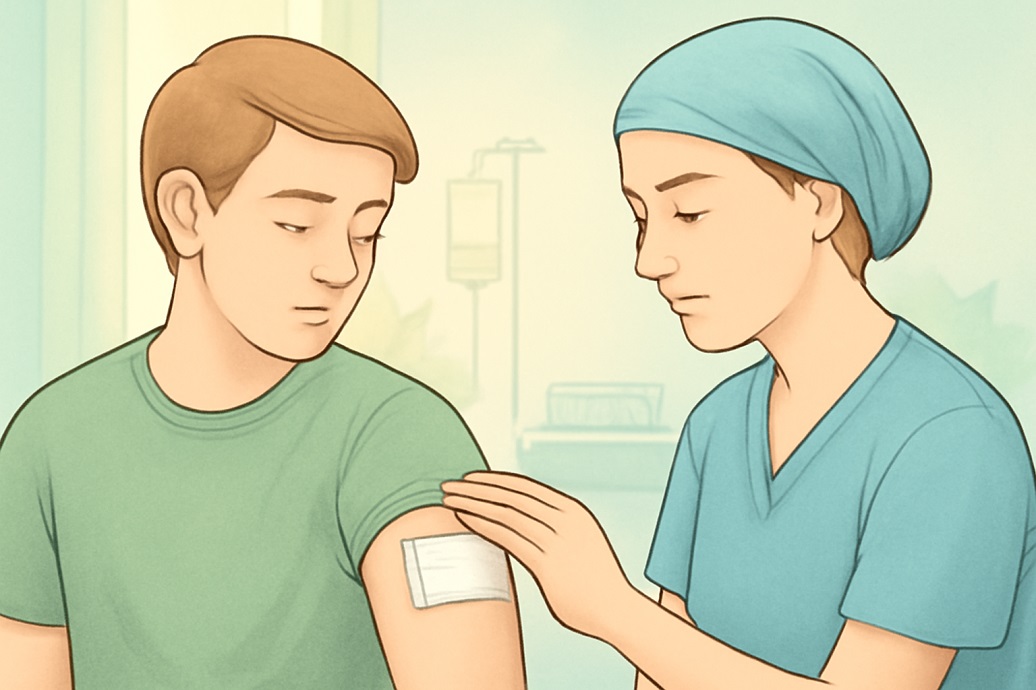
Aftercare & Recovery
After debridement, proper wound care is essential:
- The area must be kept dry and clean.
- Dressings must be changed regularly.
- Antibiotics should be prescribed in case of an infection.
- The patient must watch for signs of re-infection, such as redness, swelling, heat, or
discharge.
Most people begin to see noticeable improvement in healing after debridement.
Final Thoughts
Whether it’s a chronic wound, a serious burn, or a skin infection, debridement can be a life- saving and healing-boosting step. One must consult a wound care specialist to see if debridement is required if a wound is not healing.
